
“Digital photography killed Kodak’s business.”
“Netflix put Blockbuster out of business.”
“Amazon put Toys “R” Us out of business.”
When an iconic brand goes under, the blame game always commences.
The truth is, Amazon didn’t put Toys “R” Us out of business. Neither did Target or Wal-Mart.
Toys “R” Us put Toys “R” Us out of business.
My colleague Warren Kurtzman wrote last week about how essential it is for every brand to have a clearly defined base position. But is that enough?
What’s a better base position than “the photography company”? Or “the movie store”? Or “the toy store”?
Kodak, Blockbuster and Toys “R” Us didn’t just have strong positions in their categories, they owned the dominant positions. The problem is, each of these brands lacked positive brand depth beyond their base positions.
An engineer at Kodak actually invented digital photography. In 1975. Navigating the consumer through the digital space using the brand equity of Kodak moments would have been a perfect and natural complement to its base position. Unfortunately, Kodak couldn’t see beyond its history as a film company, and competitors swooped in.
Blockbuster had an incredible, dominating base position. Unfortunately, it had negative brand depth in the form of late fees, which left it vulnerable. By the time Blockbuster removed late fees, it was too late.
If Blockbuster had entered the DVD-by-mail category or streaming category first, the company would quite likely still be around. Blockbuster had the chance to buy Netflix in the early 2000s for $50 million. Today Netflix is valued over $100 billion, worth more than every media company that’s not named Disney.
Would Netflix have had that growth under the leadership of Blockbuster? Probably not, and that’s the point.
Netflix started as a DVD-by-mail company, but its base position centered around convenient entertainment delivery. All the moves and innovations Netflix has made, including doubling down on streaming and adding original programming, has been complementary to its base position. Netflix added brand depth.
Amazon started out as an online bookstore that became an online marketplace. Its moves and innovations, including ease of app use, marketing automation, customer service and free two-day delivery, have all supported its base position as an online delivery service.
Toys “R” Us had an enviable base position and an emotional connection to legions of children who wanted to be Toys “R” Us kids.
Where did the emotional connection go?
Although the road would have been challenging, Toys “R” Us could have added brand depth to its base position. It may have been through incredible marketing automation techniques (like Amazon and Starbucks) or hiring an ace social media manager (like Wendy’s). It could have been a research program that let kids test toys. It may have been partnerships with kids’ museums around the country.
Not to say any of those ideas would have definitely worked, but Toys “R” Us needed to try long before Amazon posed a significant threat.
Integrating Babies “R” Us into Toys “R” Us stores was definitely not the answer–it detracted focus from its own brand.
Last year, Toys “R” Us CEO David Brandon said the chain hoped to add playrooms where kids could try out toys and spaces for birthday parties.
Unfortunately, they never got the chance to give them a shot.
When we work with radio stations, we illustrate the base position on our Image Pyramid, but also explain the perils of a misguided Image Pyramid–which is what Kodak, Blockbuster, and Toys “R” Us all ran into.
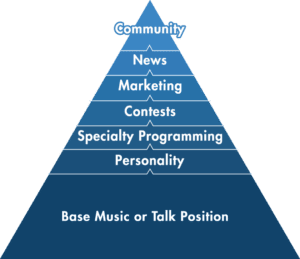
Clearly define your base position. Once you do, never stop adding brand depth.

Love the blog this week. Just as a side note, Blockbuster did envision online streaming (https://www.forbes.com/2000/07/20/mu4.html#2bda108a3541) in July 2000; unfortunately, it was a twenty year deal with Enron Broadband… and that didn’t work out so well (https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB984181374790463655). The deal was terminated less than nine months later and well… we all know what happened next.
Again, great read this week! Keep ’em coming.
Ian
Thanks, Ian! Enron Broadband. Ouch.